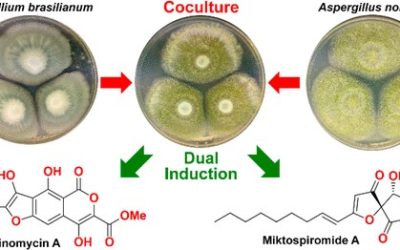
Ranjala Ratnayake, Leith J. Fremlin, Ernest Lacey, Jennifer H. Gill, and Robert J. Capon
Journal of Natural Products, 2008, 71, 403-408.
Publication Date: February 21, 2008
https://doi.org/10.1021/np070589g
Abstract:
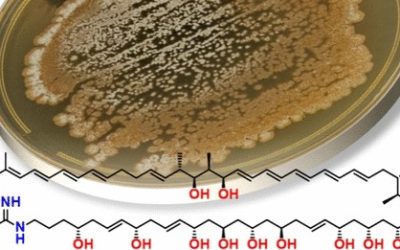
An Australian estuarine isolate of an Acremonium sp. (MST-MF588a) yielded the two known compounds 19-O-acetylchaetoglobosin D (1) and 19-O-acetylchaetoglobosin B (2), as the sole cytotoxic principles, along with the known aromatic metabolite RKB 3564S (3), and a novel family of lipodepsipeptides, acremolides A−D (4–7). Structures were assigned to 4–7 on the basis of detailed spectroscopic analysis and chemical derivatization and by application of a new C3 Marfey’s method for amino acid analysis.