Benjamin R. Clark, Robert J. Capon, Ernest Lacey, Shaun Tennant and Jennifer H. Gill
Organic and Biomolecular Chemistry, 2006, 4, 1520-1528.
Publication Date: Febuary 27, 2006
https://doi.org/10.1039/B600960C
Abstract:
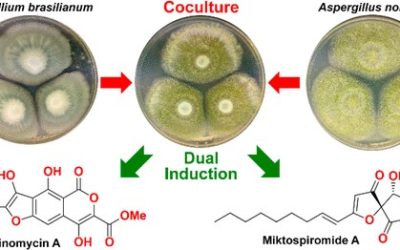
Detailed chemical analysis of the solid phase fermentation of an Australian Penicillium citrinum isolate has returned the known compounds citrinin (1), phenol A acid (6), dihydrocitrinone (7) and dihydrocitrinin (8), together with a novel cytotoxic dimer, dicitrinin A (5). Dicitrinin A (5) was determined to be a dimerised artefact of the major co-metabolite citrinin, and its structure solved by spectroscopic analysis and chemical modification. Analysis of the products encountered during the controlled decomposition of citrinin led to the discovery of additional citrinin dimers and delineated a plausible mechanistic pathway linking all monomeric and dimeric citrinin degradation products.
Available at BioAustralis: