Heather J. Lacey, Thomas J. Booth, Daniel Vuong, Peter J. Rutledge, Ernest Lacey, Yit-Heng Chooi & Andrew M. Piggott
The Journal of Antibiotics 2020, 73, 756-765
Publication Date: June 17, 2020
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41429-020-0332-3
Abstract:
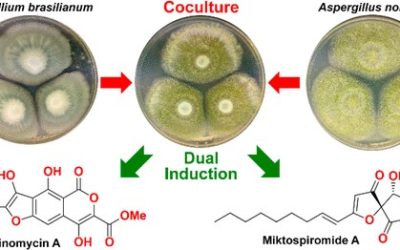
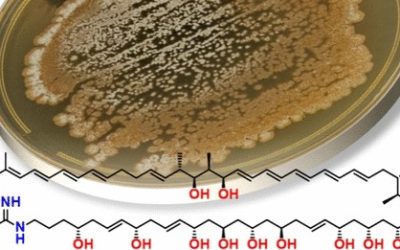
Chemical investigation of a previously unreported indigenous Australian Streptomyces strain MST-91080 has identified six novel analogues related to the oxazole-pendanted macrodiolide, conglobatin. Phylogenetic analysis of the 16S rRNA gene sequence identified MST-91080 as a species of Streptomyces, distinct from reported conglobatin producer, Streptomyces conglobatus ATCC 31005. Conglobatins B–E diverge from conglobatin through differing patterns of methylation on the macrodiolide skeleton. The altered methyl positions suggest a deviation from the published biosynthetic pathway, which proposed three successive methylmalonyl-CoA extender unit additions to the conglobatin monomer. Conglobatins B1, C1 and C2 exhibited more potent cytotoxic activity selectively against the NS-1 myeloma cell line (IC50 0.084, 1.05 and 0.45 µg ml−1, respectively) compared with conglobatin (IC50 1.39 µg ml−1).