Leith J. Fremlin, Andrew M. Piggott, Ernest Lacey, and Robert. J. Capon
Journal of Natural Products, 2009, 72, 666-670.
Publication Date: February 26, 2009
https://doi.org/10.1021/np800777f
Abstract:
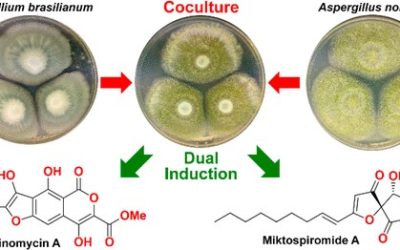
An Australian marine-derived isolate of Aspergillus versicolor (MST-MF495) yielded the known fungal metabolites sterigmatocystin, violaceol I, violaceol II, diorcinol, (−)-cyclopenol, and viridicatol, along with a new alkaloid, cottoquinazoline A (1), and two new cyclopentapeptides, cotteslosins A (2) and B (3). Structures for 1−3 and the known compounds were determined by spectroscopic analysis. The absolute configurations of 1−3 were addressed by chemical degradation and application of the C3 Marfey’s method. The use of “cellophane raft” high-nutrient media as a device for up-regulating secondary metabolite diversity in marine-derived fungi is discussed. The antibacterial properties displayed by A. versicolor (MST-MF495) were attributed to the phenols violaceol I, violaceol II, and diorcinol, while cotteslosins 2 and 3 were identified as weak cytotoxic agents.