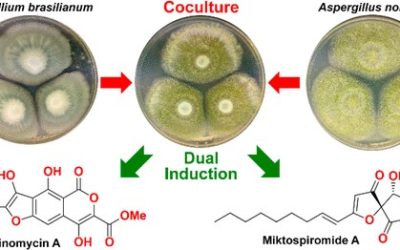
Patrick J. C. James, Daniel Vuong, Stephen A. Moggach, Ernest Lacey, and Matthew J. Piggott
Journal of Natural Products 86, 550-556.
Publication Date: March 10, 2023
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.2c01013
Abstract:
The lichen natural products pulvinamide, rhizocarpic acid, and epanorin have been synthesized and characterized spectroscopically and by X-ray crystallography. The syntheses, by ring-opening of pulvinic acid dilactone (PAD), may well be biomimetic, given the well-known occurrence of PAD in lichen. The enantiomers, ent-rhizocarpic acid and ent-epanorin, and corresponding carboxylic acids, norrhizocarpic acid and norepanorin, were similarly prepared. All compounds were assessed for growth inhibitory activity against selected bacteria, fungi, a protist, a mammalian tumor cell line, and normal cells. Rhizocarpic acid is weakly antibacterial (Bacillus subtilis MIC = 50 μg/mL) and possesses modest but selective antitumor activity (NS-1 murine myeloma MIC = 3.1 μg/mL) with >10-fold potency relative to its enantiomer (MIC = 50 μg/mL).