Nirmal K. Chaudhary, Andrew Crombie, Daniel Vuong, Ernest Lacey, Andrew M. Piggott, and Peter Karuso
Journal of Natural Products 2020, 83, 1051-1060
Publication Date: March 2, 2020
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.9b01066
Abstract:
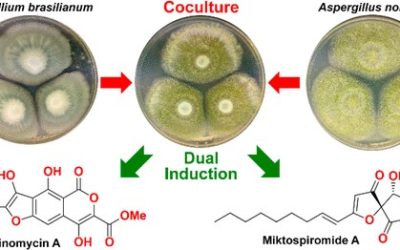
Cultivation and extraction of the fungus Talaromyces stipitatus led to the isolation of five new oxyphenalenone–amino acid hybrids, which were named talauxins E, Q, V, L, and I based on the corresponding one-letter amino acid codes, along with their putative biosynthetic precursor, duclauxin. The rapid reaction of duclauxin with amino acids to produce talauxins was demonstrated in vitro and exploited to generate a small library of natural and unnatural talauxins. Talauxin V was shown to undergo spontaneous elimination of methyl acetate to yield the corresponding neoclauxin scaffold. This process was modeled using density functional theory calculations, revealing a dramatic change in conformation resulting from the syn elimination of methyl acetate.